The electronic ID
What is an Electronic ID?
The electronic ID card is a document issued by the General Directorate of Police (Ministry of the Interior). In addition to physically accrediting the personal identity of its owner, it allows:
- Crediting electronically and unequivocally their identity.
- Sign digitally Electronic documents, granting them one legal validity Equivalent to the one provided by the handwritten signature.
The DNIe incorporates a small integrated circuit (chip), which contains the same data printed on the card (personal data, photograph, digitised signature and digitised fingerprint) along with the certificates of Authentication and of Electronic Signature.
In this way, any person will be able to carry out multiple online actions safely with the Public Administrations, with public and private companies, and with other citizens, at any time and without having to travel or queue.
Electronic Certificates in the DNIe
With the electronic ID, two certificates are obtained:
- Certificate of Authentication: It electronically guarantees the identity of the citizen when making a telematic transaction. This Certificate ensures that electronic communication is made with the person who claims to be, with the identity certificate and the private key associated with it.
- Certificate of Signature: It allows the signing of procedures or documents, replacing the handwritten signature. Therefore, it guarantees the identity of the subscriber and the holder of the private identification and signature key.
For more information about What is an Electronic ID, visit the page of the National Police Force or eID Basic Reference Guide.
You can learn more about certificates in the Electronic Certificates section.
The electronic certificate
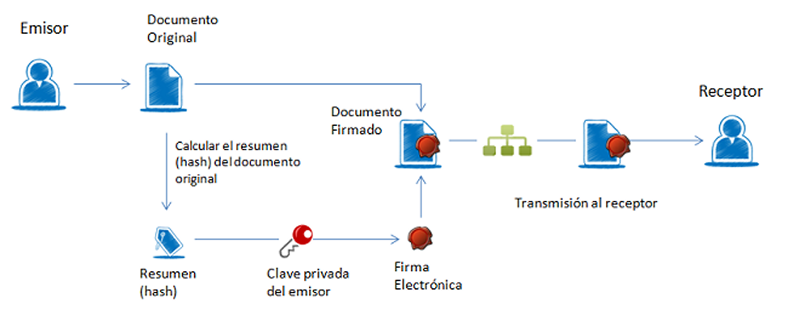
The basic process followed for electronic signatures is as follows:
- The user has an electronic document (a spreadsheet, a pdf, an image, even a form on a web page) and a certificate that belongs to him and identifies him.
- The application or digital device used for the signature summarizes the document. The summary of a large document can be as simple as a few lines. This summary is unique and any modification of the document also involves a modification of the summary.
- The application uses the private key to encode the summary.
- The application creates another electronic document that contains that encoded summary. This new document is the electronic signature.
The result of this whole process is an electronic document obtained from the original document and the signer’s keys. The electronic signature, therefore, is the same resulting electronic document.
Remember:
The electronic signature is the resulting electronic file or document. This is the document valid for legal purposes and the one that you must keep. Any printing or graphic representation that is made of it is only valid in the terms determined by the recipient of the signature. In general, in this case, the printed signature should contain a CSV or Secure Verification Code that allows the printed copy to be contrasted with the electronic original.
How to use the DNIe?
Technical requirements
For the use of the ID, it is necessary to have certain hardware and software elements that will allow us to access the card chip and, therefore, the use of the certificates contained in it.
While the DNIe only allows contact access, the DNI 3.0 has a Dual Interface chip, which also allows wireless connection through the NFC antenna.
For use by contact you need:
- A personal computer.
- A smart card reader. There are different implementations, either integrated into the keyboard, external (connected via USB) or through a PCMCIA card.
For contactless use you need an NFC-enabled device that complies with ISO 14443, type A or B, as DNI 3.0 is compatible with both implementations of ISO 14443. This device can be a Smartphone, a tablet or an NFC reader.
In terms of software, the electronic DNI is compatible with the currently existing operating systems, as well as with the different browsers. Here you can get more information.
Technical Requirements: In order to be able to interact properly with the cryptographic cards and with the electronic DNI, your computer has to have installed some ‘pieces’ of software called cryptographic modules.
In an environment Microsoft Windows, the computer must have installed a service called "Cryptographical ServiceProvider" (CSP).
In the environments UNIX/Linux or MAC It is possible to use the DNIe through a cryptographic module called PKCS#11.
On the website of the electronic DNI, in the section Download Area You can find the information to install the DNI on both Windows systems and Linux and MacOS computers
Renewal of the DNIe and the Certificates
- Renewal of the DNIe. The renewal will be carried out through the physical presence of the holder, who must pay the fee and provide the corresponding documents. The ID must be renewed within the last 90 days of validity.
- Renewal of the certificates. Certificates can be renewed in a period of time ranging from 30 days ago from the expiry date of the certificates until the expiry of the physical medium (DNIe Card).
To renew your DNIe: According to Law 59/2003 of Electronic Signature if more than 5 years have passed since the first identification, the renewal, through the Points of Updating of the DNIe, will require the prior personation of the citizen before an official of the Office of Expedition.
The validity of the certificates contained in the card chip of the Electronic ID es de 30 months. (Article 12. Validity of electronic certificates, RD 1553/2005, of 23 December)
Denunciation and revocation of the Certificates
In case of loss or subtraction of the DNIe it's mandatory personalise at a DNI Expedition Office to report your loss.
La revocation of the electronic certificates of your DNIe will be carried out immediate form to the processing of each verified request as valid.
