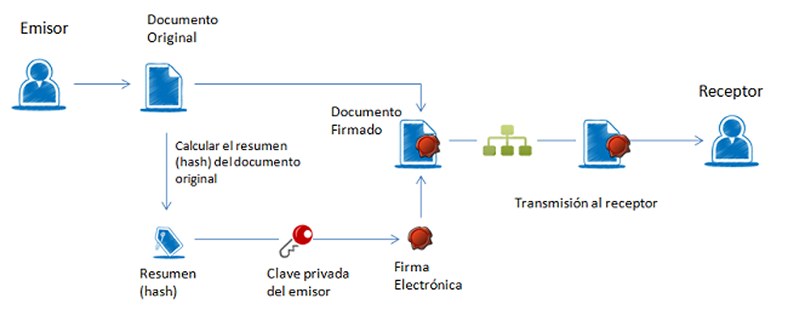
The electronic signature is a set of electronic data that accompany or are associated with an electronic document and whose basic functions are:
- Identify the signatory unequivocally.
- Ensure the integrity of the signed document. It ensures that the signed document is exactly the same as the original and that it has not been altered or manipulated.
- Ensure the non-repudiation of the signed document. The data used by the signer to make the signature are unique and exclusive and, therefore, subsequently, you cannot say that you have not signed the document.
The legal basis for electronic signatures is currently regulated by Regulation (EU) No 910/2014, known as the eIDAS Regulation, which establishes a common framework for electronic signatures, trust services and electronic identification throughout the European Union. In Spain, this regulation is complemented by Law 6/2020, on trusted electronic services, which make it possible to carry out legal transactions through electronic means, guaranteeing the security and reliability of these. They include the creation, verification and validation of electronic signatures, time stamps, certified electronic delivery services, among others.